In 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that there were approximately 30,600 long-term care facilities in the United States with over 1 million beds and 818,800 residents. According to the National Institute on Aging, a long-term care facility can incorporate any of the following:
- Board and care homes
- Assisted living facilities
- Nursing homes
- Continuing care retirement communities
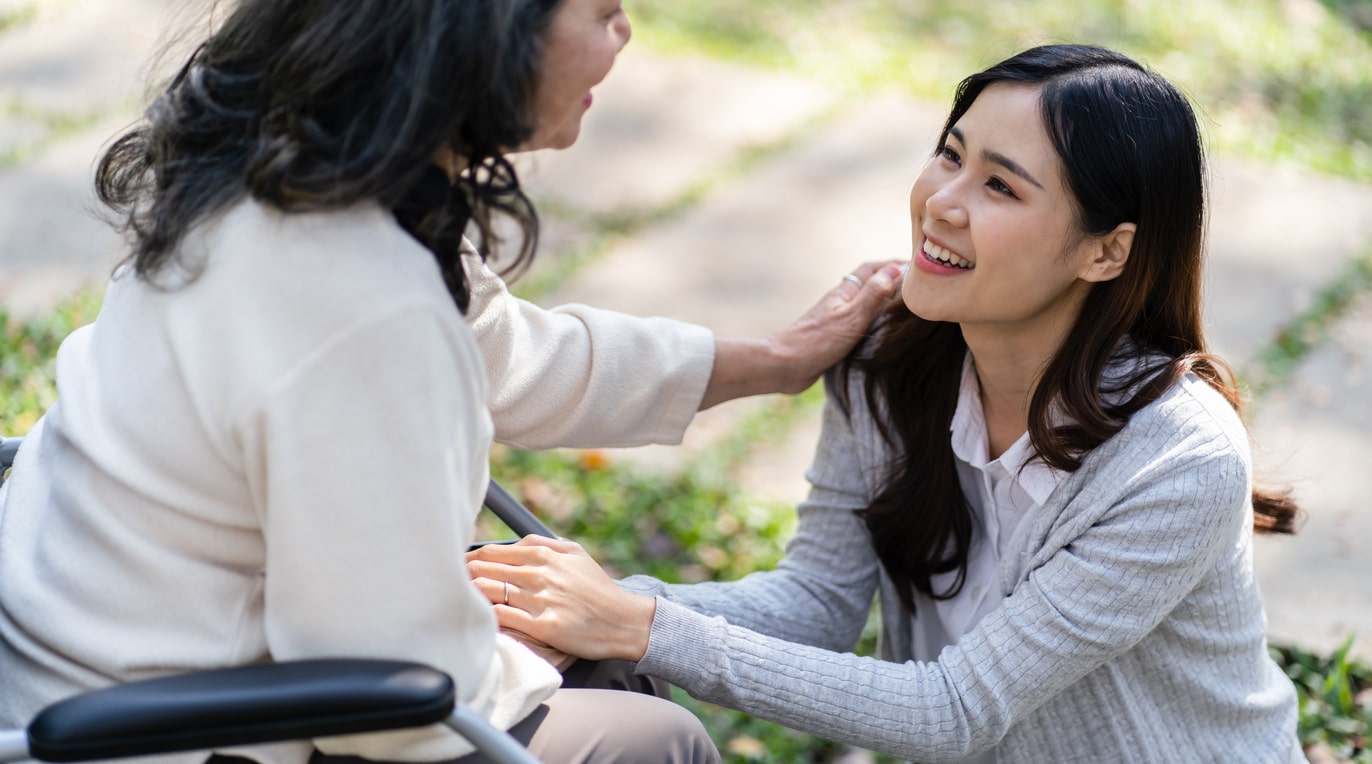
Whatever name they’re referred to as, long-term care facilities provide residential, medical, and personal care to elderly or disabled people. In doing so, these facilities have a crucial responsibility to ensure the patients are well taken care of. This includes maintaining a safe and healthy environment.
Here are five safety and health tips for your long-term care facility:
Make Cleanliness and Hygiene a Top Priority

Whether it’s a standard hospital or long-term care facility, all medical institutions are prone to attracting germs and diseases. Not only are there numerous sick people residing in long-term care facilities, but people are often close together in common areas, making the spread of germs more probable.
Communicable viruses and diseases, such as COVID-19, can easily spread throughout a long-term care facility. COVID outbreaks are common in residential care facilities. One statistic puts the COVID death rate in nursing homes at 23 times higher than the death rate for individuals 65 and over outside of nursing homes.
It’s essential to take precautionary steps to decrease patients’ risk of COVID and other communicable diseases and viruses in long-term care facilities. Some ways to accomplish this include:
- Sanitize common areas, bathrooms, and private rooms regularly
- Ensure patients receive regular and thorough hygiene care
- Put handwashing and hygiene policies in place for staff.
- Wash and cover cuts and wounds as appropriate
- Follow CDC guidelines for COVID protocol
Create an Easy-to-Navigate Long Term Care Facility

Elderly people are more likely to suffer from a fall. In fact, the National Institute on Aging states that more than one in four people who are over the age of 65 fall annually. In addition, the risk of falling rises with age. Since most residents of a long-term care facility are elderly and may have medical needs, there is an increased risk of falling.
Caregivers must take precautions to protect patients in long-term care facilities from falling. Residential care facilities can implement the following tips to prevent patient falls:
- Assist patients using ambulatory devices for walking
- Remove all clutter from walkways and passages
- Have soft surfaces throughout the facility to break a fall if it occurs
- Don’t let patients wander around when on disorienting medication
Ensure Long Term Care Patients Have Proper Nutrition
Patients with a poor diet may suffer from malnutrition and/or dehydration, which is dangerous for people in long-term care facilities. Malnutrition can lead to a host of problems in the elderly. Some of these problems include the risk of infection, slower wound healing, delirium, slower recovery from illness, and risk of death. Delirium is one of the top problems in long-term care facilities.
Planning healthy and nutritious meals at long-term care facilities will ensure the patients don’t become malnourished, ill or possibly delirious. Some patients may require a special diet, especially if they are taking certain medications that affect their ability to absorb nutrients.
Regularly Move Immobile Patients
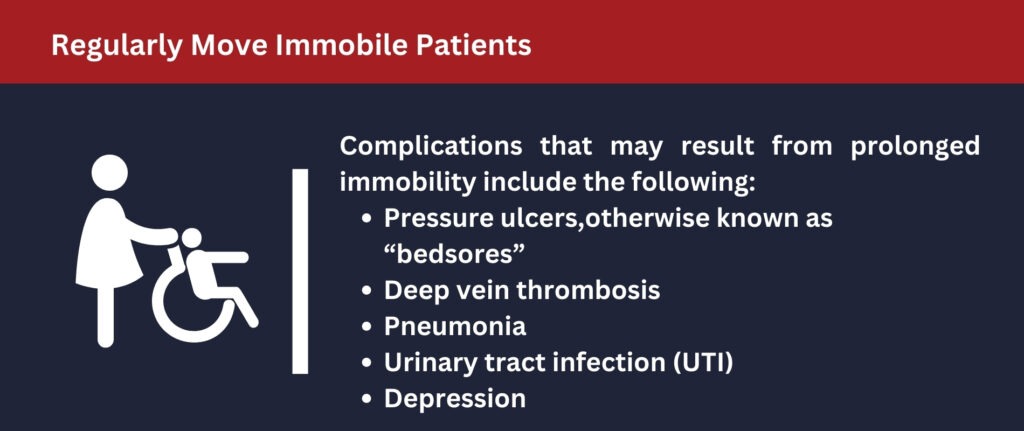
Some patients residing in long-term care facilities may be confined to their beds for long periods of time. There is a range of conditions and reasons that may hinder them from experiencing a full range of motion.
Patients experiencing immobility must be moved regularly because they are at greater risk of health complications than other patients. Some of these health complications that may result from prolonged immobility include the following:
- Pressure ulcers,otherwise known as “bedsores”
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Pneumonia
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Depression
Medical staff can adhere to a schedule of turning patients in their beds from one side to the other to prevent medical complications, such as pressure ulcers. Other methods can be used to help depressed patients.
Put Medication Protocols in Place
According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, adverse drug events in long-term care facilities are a common occurrence. One study revealed that medication errors accounted for almost 10 per 100 residents. The study also concluded that approximately 40% of these adverse drug events were considered preventable.
Since most people staying in a long-term care facility receive medication, it’s critical that medical staff take steps to protect their patients. Although errors are bound to happen, here are a few things that long-term care facilities can do to decrease the number of these medication mistakes:
- Make sure nurses are trained in medication dispensation
- Put protocols in place for dispensing prescriptions, such as using a checklist, double-checking times, and/or keeping a strict log
- Use a medication interactions database to check all prescriptions
- Create an accountability system by having the person who dispenses the medication sign off on it
By following these tips, your long-term care facility can ensure the health and safety of patients.